You may be wondering: What is feline infectious peritonitis (FIP)?
In fact, feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is a chronic, progressive, and fatal disease caused by feline coronavirus infection. The virus triggers an abnormal immune system response in cats, leading to peritonitis and the production of large amounts of ascites.
Symptoms of FIP may vary from individual to individual, but usually include loss of appetite, lethargy, weight loss, persistent and recurring fever, pale mucous membranes, anemia, jaundice, etc. Feline infectious peritonitis can be divided into two types, dry peritonitis and wet peritonitis.
Dry peritonitis:
When the virus invades the eye, corneal edema, sedimentation, aqueous humor becomes red, fibrin clots appear in the anterior chamber, inflammation of the iris and ciliary body, and retinal detachment occur.
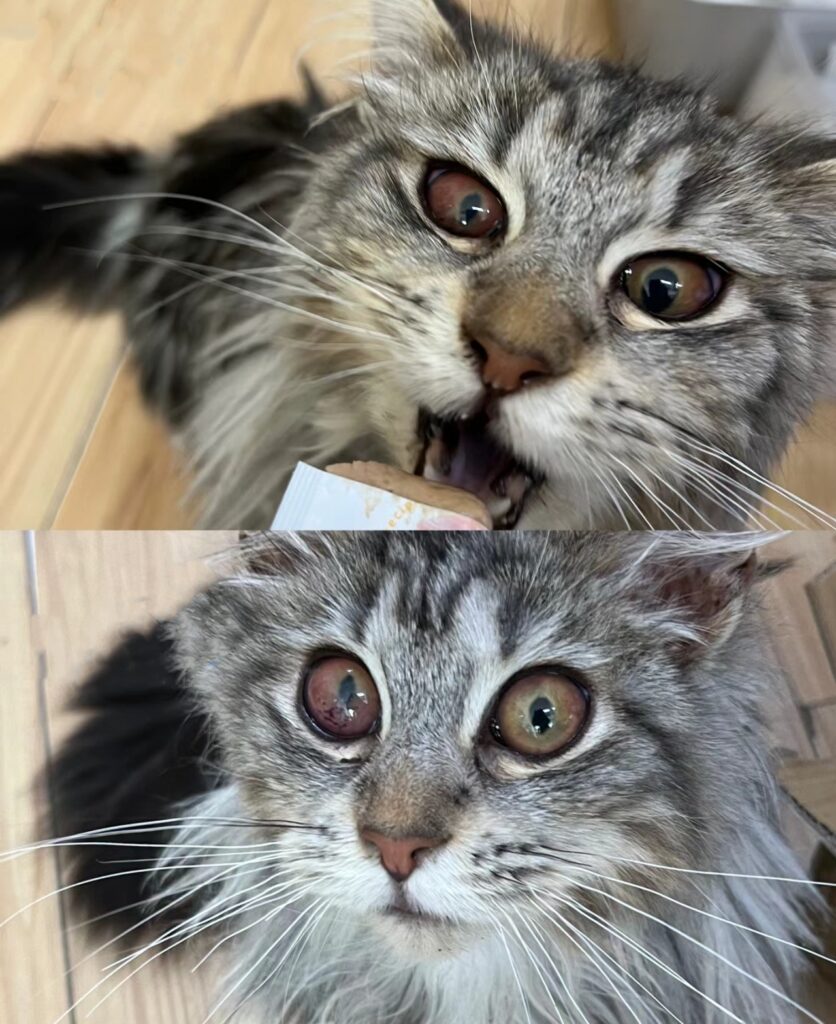
When the virus invades the central nervous system, it can cause movement disorders, disorders, back allergies, and spasms.
When the liver is damaged, it becomes enlarged and jaundice occurs, and when the kidneys fail, they become enlarged.
Wet peritonitis:
In the early stage, the sick cat had a body temperature of 39.7-41.1 degrees, was listless, anorexic, lost weight, and had an increased number of white blood cells.
After 1-6 weeks, the abdomen will become enlarged (female cats are often mistaken for pregnancy). In severe cases, 1000 ml of fluid can be released, resulting in difficulty breathing, anemia, and failure.

Diagnosis of FIP is usually based on clinical signs, blood tests, and examination of ascites fluid. The characteristic manifestations of ascites, such as high protein content and increased number of white blood cells, as well as abnormalities in the Albumin to Globulin Ratio, are important indicators of diagnosis.
Treatment recommendations for cats unfortunate enough to have FIP are:
Supportive care:
- Provide a high-quality diet: Provide cats with feline infectious peritonitis a high-protein, high-energy diet to help maintain their strength and nutritional status. Consult your veterinarian about appropriate dietary options.
- Hydration: Making sure your cat drinks enough water will help prevent dehydration. If your cat is reluctant to drink water of its own accord, consider using a syringe or dropper to give it water.
- Keep body temperature stable: Keep your cat’s living environment at a suitable temperature and avoid cold or overheating. Cats can be provided with warm blankets or cushions to rest on.
- Provide a comfortable environment: Create a quiet, comfortable and clean living environment for cats to reduce stress and stimulation.

Medical:
- Antibiotics: If your cat develops an infection, the infection can be treated with appropriate antibiotics.
- Diuretics: If your cat develops ascites, diuretics can be used to help reduce the symptoms of ascites.
- Antiviral drug: “gs441524” has a strong inhibitory effect on feline infectious peritonitis virus (FIPV). It is a nucleoside analog that achieves therapeutic purposes by interfering with viral RNA replication.
Immunomodulatory treatment:
- Ascites Aspiration: Consider ascites aspiration if the ascites is severely affecting your cat’s breathing or comfort. This can temporarily relieve abdominal pressure but does not cure the disease.
It should be emphasized that FIP is a serious disease and the treatment effect is often unsatisfactory. Each cat’s condition may be different, so a treatment plan will need to be developed on an individual basis. It is important to work closely with your veterinarian to develop a treatment plan that is best for your cat and to provide the care and support your cat needs. At the same time, regular review and monitoring of changes in condition are also necessary. Finally, I hope all the cats in the world will be cute and not sick.